Top Medical Spa in Österreich
Medizin – die erste Säule
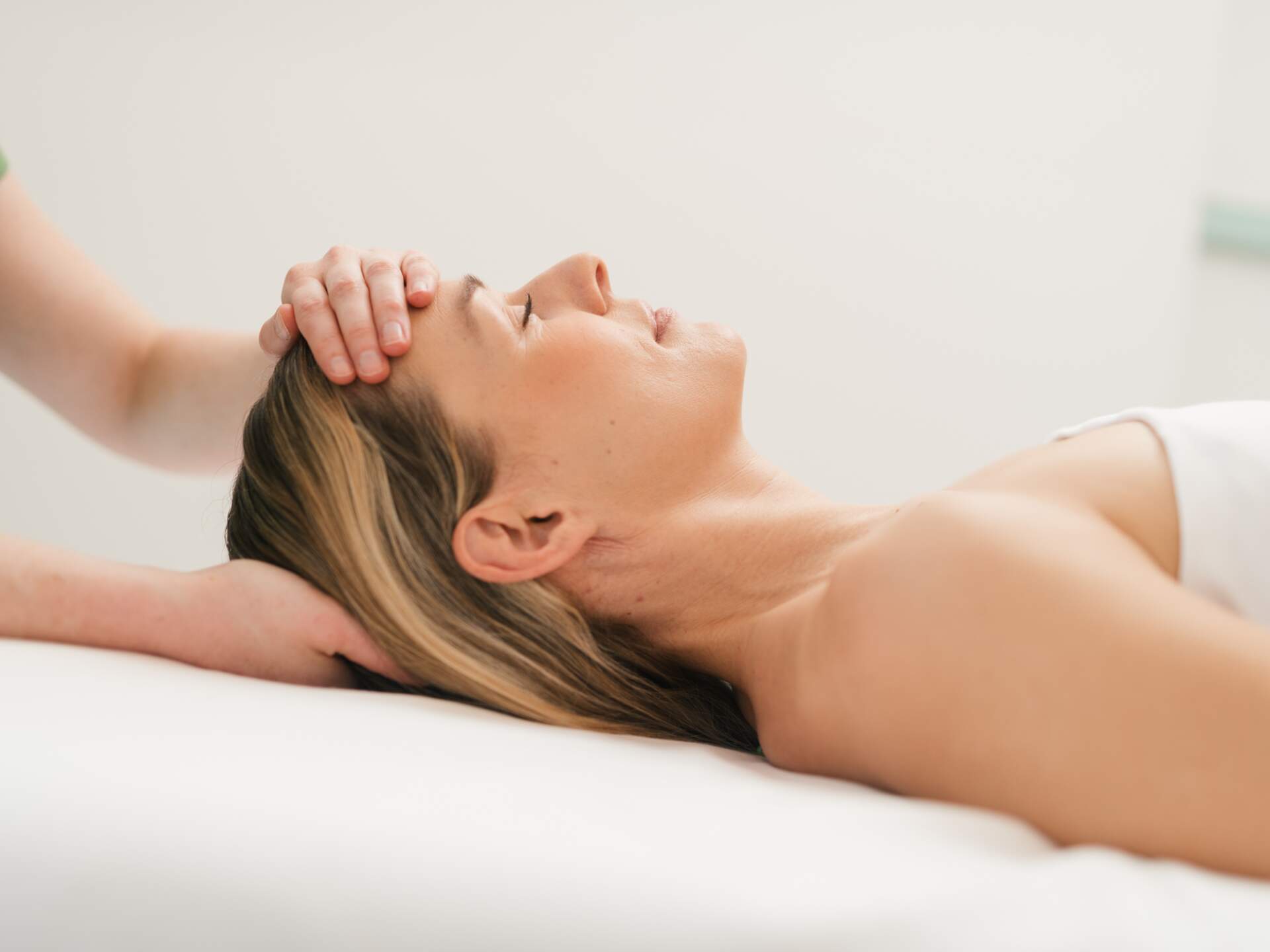
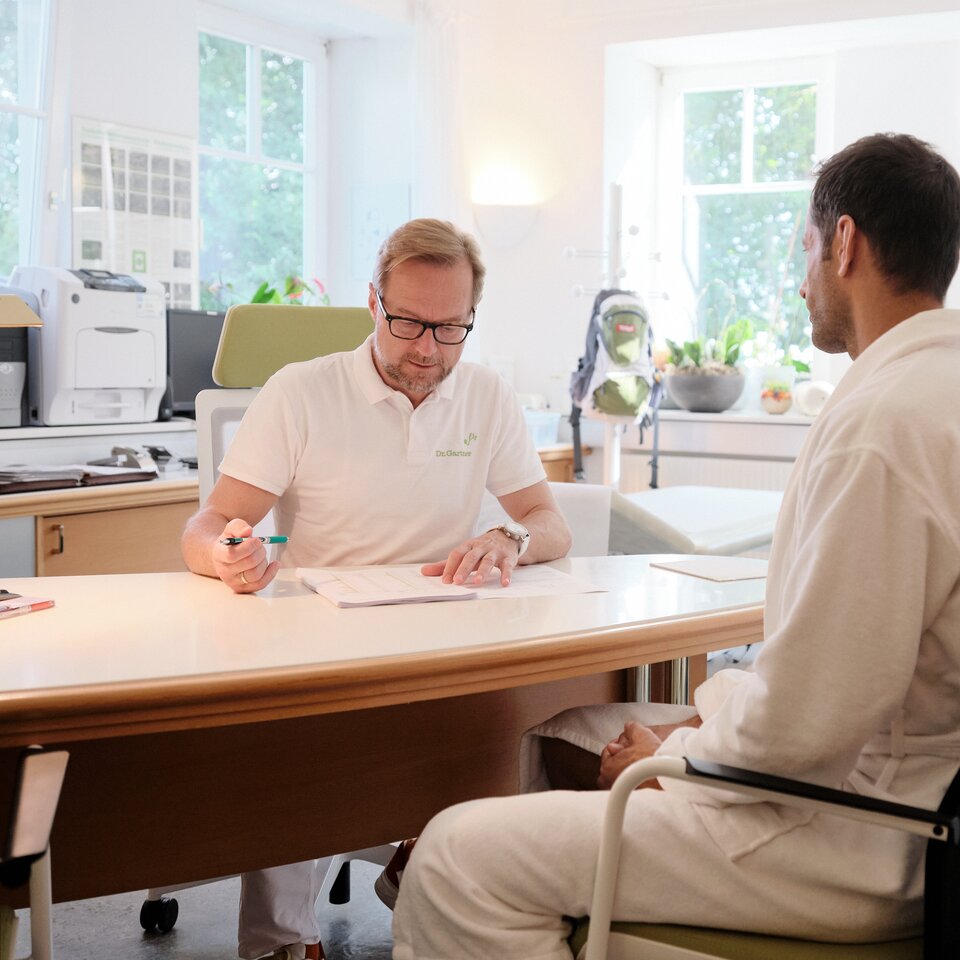
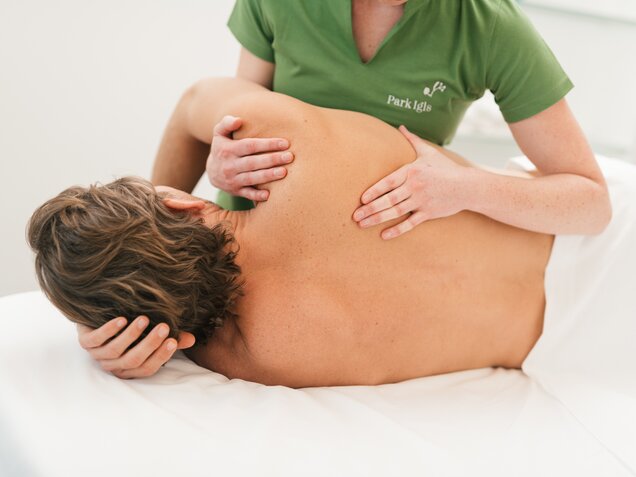
Die Mayr-Ärzte und -Ärztinnen im Medical Spa Resort kombinieren Schul- und Komplementärmedizin mit Psychologie sowie Bewegungstherapie und betrachten die menschliche Gesundheit aus allen Blickwinkeln. So wird der Gast individuell in ein passendes Programm eingeführt und nachhaltig in eine gesunde Zukunft geleitet. Dabei steht dem Gast eine zeitgemäße und ausgezeichnete Bandbreite an Diagnostiken, Therapien und ärztlichen Leistungen zur Verfügung.
Die Moderne Mayr-Medizin
Prävention & Therapie
Eine regelmäßige Entgiftung des Organimus ist von enormer Bedeutung für eine bessere Lebensqualität in einer Zeit, die von Stress, mentaler Überlastung und mangelhafter Ernährung geprägt ist. Die Moderne Mayr-Medizin schafft mit Prävention und Therapie einen willkommenen Ruhepol und zieht sich wie ein roter Faden durch das gesamte Behandlungskonzept, von Ernährung über Bewegung bis zur Regeneration.
Das medizinische Angebot im Park Igls
Den Mensch ganzheitlich betrachten
Die Herausforderungen für den Körper sind so individuell wie der Mensch selbst. Das umfassende Angebot aus ärztlichen Leistungen, Diagnostiken und Therapien im Park Igls Medical Spa Resort liefert professionelle Analysen und Lösungsansätze und macht das Park Igls zu einem führenden Medical Spa in Österreich.
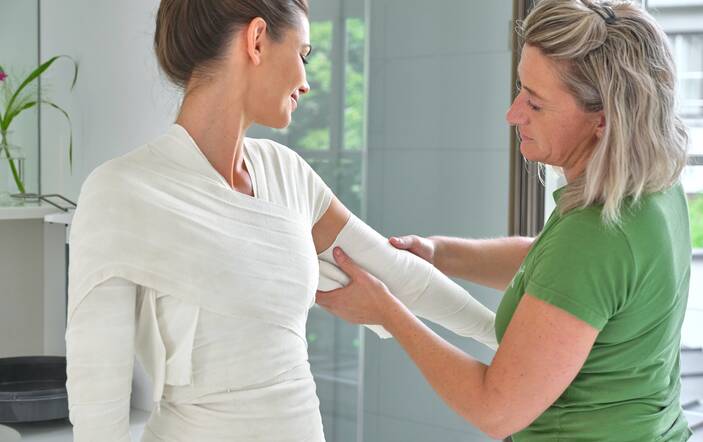
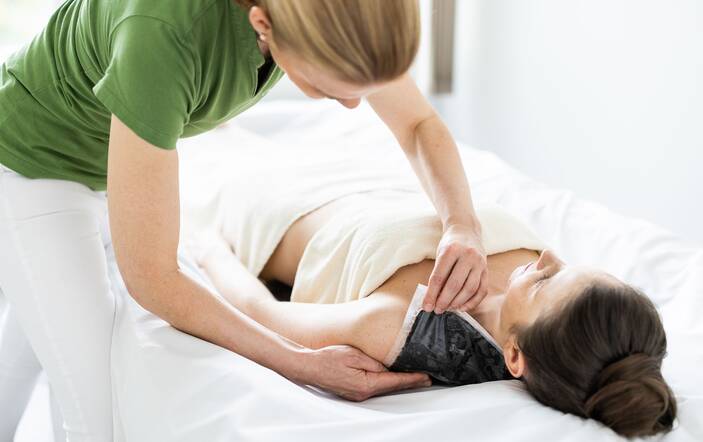





Vertiefen & informieren
Der Park-Igls-Blog
Medical Wellness lässt sich als ein Maßnahmenpaket zusammenfassen, das von Ärztinnen und Ärzten individuell für den Gast geschnürt sowie in der Ausführung begleitet wird. Dies kann im Rahmen einer Kur, aber auch als Urlaub umgesetzt werden. Die Zielsetzung beinhaltet:
- nachhaltige Verbesserung der Lebensqualität, des subjektiven Gesundheitsempfindens und des objektiven Gesundheitszustandes des Gastes
- Anleitung zur eigenverantwortlichen Prävention und Gesundheitsförderung durch den Gast
- Motivation des Gastes zu einem gesundheitsbewussten Lebensstil
Der Begriff Medical-Wellness-Hotel wird mittlerweile sehr verbreitet und leider inflationär verwendet. Es sollte aber nur dann als Beschreibung für ein Hotel genutzt werden, wenn wie im Park Igls Medical Spa Resort folgende Faktoren vorhanden sind:
- ein oder mehrere Ärztinnen und Ärzte vor Ort im Hotel
- hervorragend ausgebildete Fachkräfte
- medizinische Erst- und Abschlussuntersuchungen
- tägliche Fitness- und Bewegungsprogramme
- ausgewogene und gesunde Küche
- attraktive Lage und Umgebung
- vielfältige Sportmöglichkeiten
- Fokus auf das Anleiten der Gäste zu einem gesunden Lebensstil